Conference Notes 10-26-2016
Felder/Munoz Oral Boards
Case 1. 26 yo female with weakness and muscle pain. Patient is tachycardic. Patient had recent diarrheal illness. PMH is positive for hyperthyroidism. Patient has not been taking thyroid medications. Labs show K=1.5.
*Thyrotoxic Periodic Paralysis. Precipitating causes include heavy exercise and high carbohydrate meal.
Patient treated with propranolol, potassium. Treat hypomagnesemia. PTU, potassium iodide.
Harwood comment: Case reports are very convincing that propranolol is the most effective treatment for hypokalemic periodic paralysis. These patients are not actually potassium depleted. Be cautious with potassium repletion to avoid rebound hyperkalemia.
Case 2. 19 yo male with history of diarrhea. Febrile. HR=107BP 70/40 RR=12. Patient has myalgias. No PMH. Patient has diffuse erythematous rash and a buttock abscess. Diagnosis is toxic shock secondary to abscess. Patient treated with IV Clindamycin (clindamycin blocks toxin production) and Vancomycin , IV fluids, IV norepinephrine. Abscess was drained. Update tetanus if needed.
*Toxic Shock rash. Toxic shock is secondary to exotoxin released by staph aureus.
Case 3. 4yo male with barky cough. O2 sat=99%. Parents note recurrent episodes of croupy cough over last 2-3 weeks. No fever. Diagnosis is aspirated foreign body. Treatment is ENT or pulmonary consultation for bronchoscopy.
*Lateral decubitus film shows persistent hyper-expansion despite being dependent (down side). That is suspicious for aspirated FB on right side causing air trapping. Lateral decubitus films in general are unreliable for identifying FB. Mila made the point that if you suspect aspirated FB you need to arrange a bronchoscopy.
RLT Recruiting Update
Lambert Ultrasound in Trauma
*FAST and E-FAST exams.
*Pelvic fluid on FAST is posterior to bladder.
*Blood in Morrison’s pouch
The left kidney is more posterior and cephalad than the right kidney. To visualize the left kidney, put the probe almost on the surface of the bed and move it toward the patient. The left kidney is that far posterior.
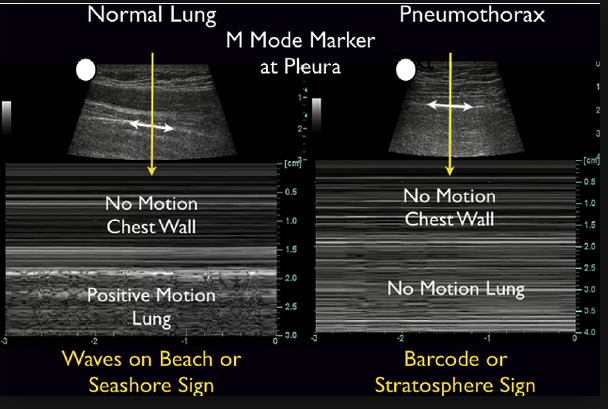
*M-Mode images of normal lung and pneumothorax. When getting lung images, Mike recommends staying just lateral to the sternum.
*Hemopericardium on FAST exam. Mike made the point that tamponade is a clinical diagnosis. You can’t diagnose pericardial tamponade by ultrasound images alone. Suggestive signs of pericardial tamponade are hypotension, tachycardia, pericardial fluid, and RV compression or diastolic collapse on US.
Lambert Gallbladder Ultrasound
When identifying the gallbladder in the longitudinal plane you want to visualize the gallbladder with the main lobar fissure and the right portal vein all in the same image field.
*GB, main lobar fissure, and right portal vein
*Gallstones with shadowing
*Wall Echo Shadow WES sign. The duodenum can look like the WES sign but it will have peristalsis to differentiate it from the GB.
*Dirty shadow of duodenum vs Clean shadow of gallstones
Lambert Kidney Ultrasound
Special Thanks to Sean Motzny and all the Outstanding EMS Providers for an outstanding CART training Exercise last week!