Herron/Marshalla Oral Boards
Case 1. Patient presents with sore throat and difficulty breathing.
*Epiglotitis on lateral neck x-ray and on video laryngoscopy. (Bitner, Annals EM 2007) This x-ray image has both the "thumbprint" sign and the vellecula sign where the vellecula air column does not reach the hyoid bone.
Patient was managed with IV ceftriaxone, IV steroids and consultation with ENT & Anesthesia for OR intubation. Adult infection is more likely to be due to non-HIB organism.
Case 2. 16 yo male presents with altered mental status, hypotension and tachycardia. No fever. He appears intoxicated. Dad found patient lying on the floor of the garage. Dad suspected the patient may have drunk anti-freeze. Labs show anion gap metabolic acidosis and osmolal gap.
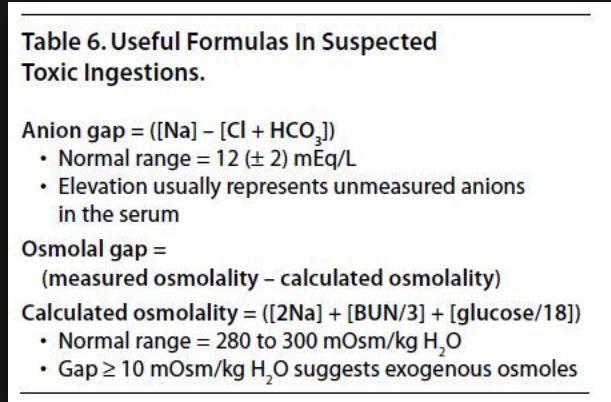
*Anion and Osmolal Gap Calculations
Treatment was IV fomepizole. Nephrology was consulted for dialysis. IV bicarb is indicated for severe acidosis. You can also give pyridoxine as a key co-factor for metabolism.
*Ethylene glycol metabolism
Case 3. Male presents with a headache following a MVC. Patient’s vehicle was struck from the rear. Patient had transient loss of consciousness for a few seconds. Key PMH is the patient has hemophilia A.
Critical management is to get Factor 8 replacement therapy started as soon as possible. For boards, always give Factor 8 prior to getting CT head. In real life, many times you can get a CT while pharmacy is getting the Factor 8 prepared. Patient has sign of intra-cerebral hemorrhage on CT. You want to get Factor 8 level to 100% by giving 50u/kg for any head injury (bleed or no bleed).
Lambert Soft & MSK Tissue Ultrasound
Only 15% of wood FB’s are visualized on x-ray. Ultrasound has much higher sensitivity for wood FB’s.
*Wood FB on ultrasound.
*Cellulitis on ultrasound. Note the “cobblestone” appearance of the tissue.
*Abscess on ultrasound. To help differentiate from cellulitis or other process, Mike compresses the suspected abscess cavity and looks for swirling or movement of the fluid in the cavity.
*Necrotizing fasciitis. Air in the soft tissue is pathognomonic for Nec Fasc. Air on ultrasound is demonstrated by hyperechoicarea (Arrows) with posterior shadowing.
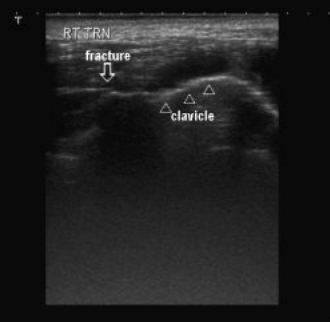
*You can also diagnose fractures with ultrasound. You can identify a cortical disruption. This is a clavicle fracture.
*97% of rotator cuff injuries are supraspinatus tears. To visualize this tendon, have the patient put their hand in their pant’s back pocket. Place the probe on the antero-lateral aspect of the humeral head and aim the probe at the ipsilateral ear.
*Quadricep tendon rupture
*Achilles tendon rupture
Lambert Ultrasound Guided Nerve Blocks
These techniques were too complex for me to write up in these notes. The residents practiced the approaches to these techniques in the Ultrasound workshop.
Lambert and Team Ultrasound Ultrasound Workshop