If you don't see images, scroll to the bottom and click "view in browser"
Burns/Collins Oral Boards
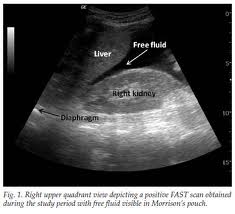
Case 1. 27yo female passed out at home. HR=62, BP=79/51, Afebrile. Patient notes abdominal pain. No PMH. Patient is taking OCP’s only intermittently and UCG is positive. Patient is persistently hypotensive despite IV fluid resuscitation. FAST exam shows free fluid in Morrison’s pouch. Diagnosis was ruptured ectopic pregnancy. Critical actions were IV Fluid and Blood resuscitation, Rapidly getting the patient to the OR, and Giving rhogam (pt was RH negative).
*Free Fluid in Morrison’s Pouch. This finding with shock and a positive pregnancy test has a positive predictive value of >90% for ruptured ectopic pregnancy.
Case 2. 27 day old child with diarrhea, fever, and “not acting right.” T=100.3, HR=160, BP=75/50 RR=46 PulseOx=96% on RA. Decreased urine output. Exam shows signs of dehydration. Patient was given 20ml/kg bolus. A septic work up including LP was begun. LP showed 200 WBC’s. Treatment for meningitis was begun. Critical actions: IV fluids, septic work-up, always consider evaluate for possible abuse, treat with antibiotics for meningitis.
Case 3. 38yo man brought in by his father. Father is concerned that patient is suicidal. Vitals are normal. Patient refused to speak with ED physician. Patient’s dad said that patient took an overdose of tylenol and threatened to shoot himself. Tylenol level was 350. Patient was treated with NAC per protocol. Patient’s duffel bag was taken away from him. When searched, his bag contained a handgun. As a note to the readers, the conversation between Dr. Burns and Dr. Collins (AKA Angry Jerry) was a classic! Dr. Burns calm, flat responses to Dr. Collins angry outbursts rivaled a comedy skit. Critical actions: Prevent patient from leaving ED, make sure patient’s possessions are taken away from him to prevent him from using a weapon in the ED. Obtain an acetaminophen level. Treat with NAC. Consult Psychiatry and Poison Control. Admit to ICU.
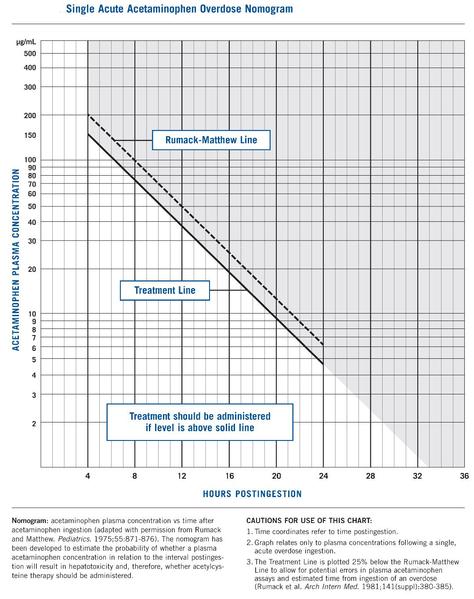
*Rumack Matthews Nomogram
The approved 20 hour IV dosing regime is complicated and is performed as follows:
Administer an initial loading dose of 150 mg/kg IV over 15 to 60 minutes (we recommend 60 minutes).
Next, administer a 4 hour infusion at 12.5 mg/kg per hour IV (ie, total of 50 mg/kg over 4 hours).
Finally, administer a 16 hour infusion at 6.25 mg/kg per hour IV (ie, total of 100 mg/kg over 16 hours).
72 hour oral protocol — The 72 hour oral (PO) dosing protocol for N-acetylcysteine treatment has been used successfully in the United States for more than 30 years, and consists of the following:
A loading dose of 140 mg/kg PO, followed by
A dose of 70 mg/kg PO every four hours for a total of 17 doses
*NAC Treatment Protocols from Up to Date
Girzadas comments: Positive FAST exam in the setting of shock and positive pregnancy test has a positive predictive value of over 90% for ectopic pregnancy. You absolutely have to LP febrile kids under one month of age. The physical exam of kids this age is unreliable for identifying a toxic or sick/meningitic neonate. You have to speak with family and or friends of psychiatric patients. The psychiatric patient’s history is extremely unreliable and can mislead you to underestimate their suicidality. You have to take the time to corroborate the patient’s history with family or friends.
There was a discussion about whether a neonate should get steroids for meningitis. According to Up to Date: Dexamethasone is not indicated in the treatment of bacterial meningitis in infants younger than six weeks or in those with congenital or acquired abnormalities of the central nervous system.
Katiyar Toxicology of Plants
Basic Classification of Plants
Alkaloids contain nitrogen. They have bitter taste. Most of them end in the three letters “ine” Strychnine, Ephedrine, Morphine.
Glycosides end in “in” Digoxin, Salicin (metabolized to asprin)
Triterpenes Tetracanabinol, urushiol (poison ivy)
Proteins/peptides/lectins: Ricin, mushrooms (extremely poisonous)
Phenols: Capsaicin, St. John’s Wart
Case: 15 month has crying and drooling after chewing on a plant
Elephant ear plants contain calcium oxylate. This can cause drooling, swelling of tongue and mouth. Eye irritation.
Poinsettia leafs have a latex sap that can irritate mouth and throat and cause vomiting. Poinsettias are not fatal, there have been no reported fatal cases.
Rhubarb leaves can cause nephrotoxicity. Don’t eat the leaves, they can damage your kidneys and cause hypocalcemia.
Jimson weed seeds if ingested can cause a significant anticholinergic toxidrome. Jimsom weed is ubiquitous along roads.
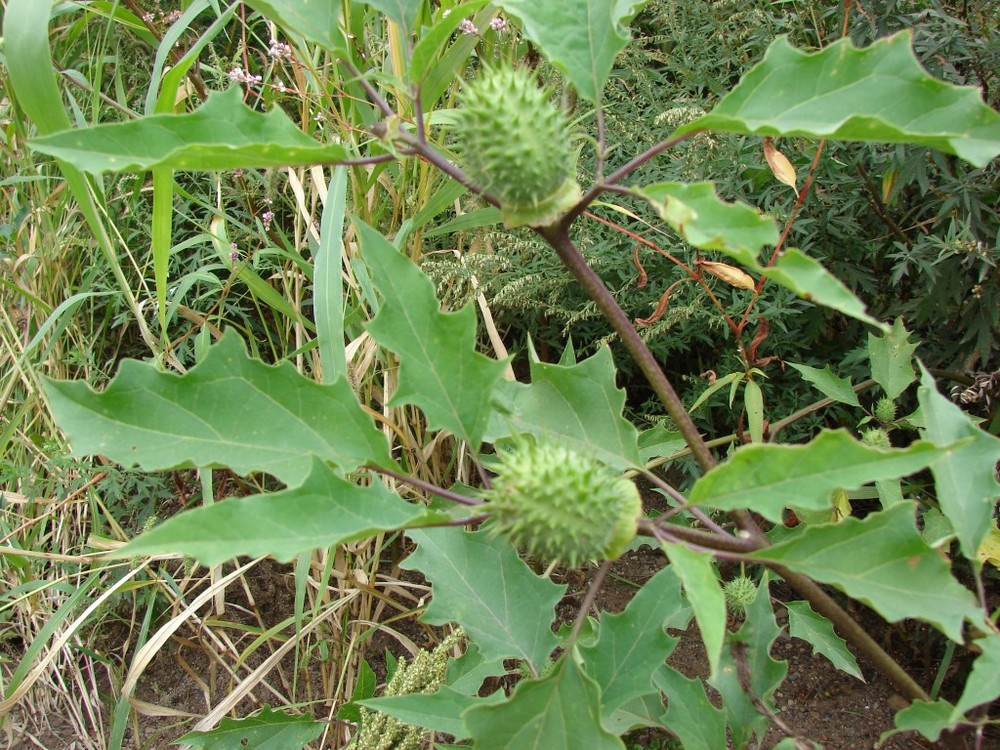

*Jimson weed
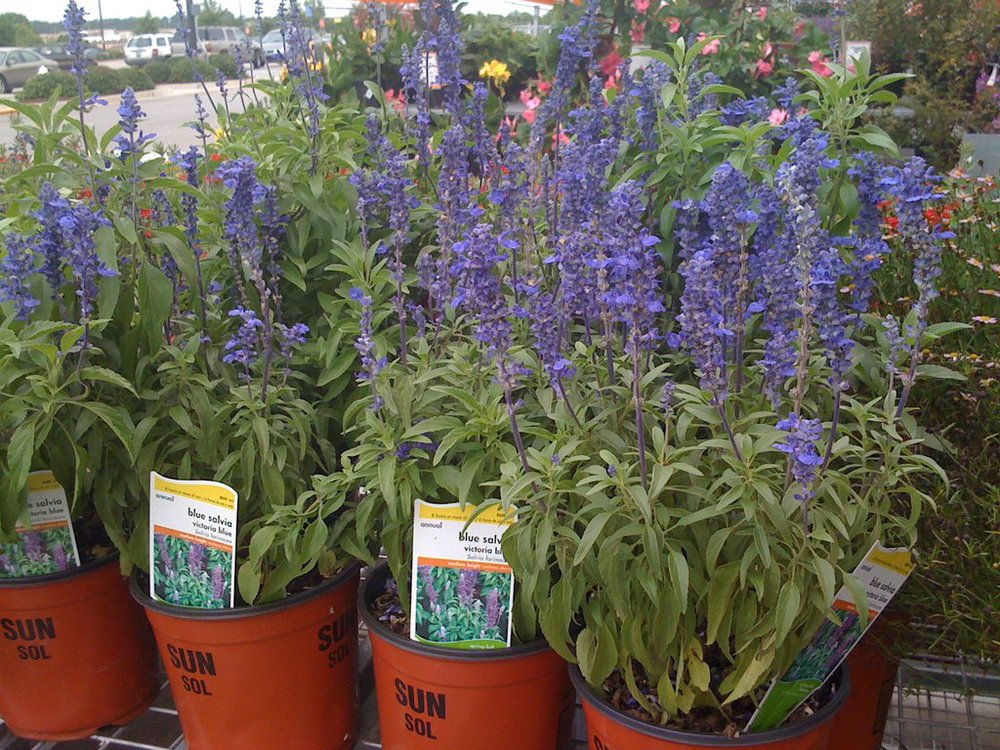

*Salvia divinorum Ingested leaves can cause hallucinations, coma, and memory loss.
Nutmeg is also hallucinogenic. Morning glory seeds are hallucinogenic.
Oleander, fox glove, and lily of the valley can cause digoxin toxicity. Patients with toxicity from these plants may need very large doses of Digibind. The lab testing of digoxin levels due to toxic plant ingestion can be falsely low.
Rhododendrons can cause hypotension, cardiac arrhythmias, and death.
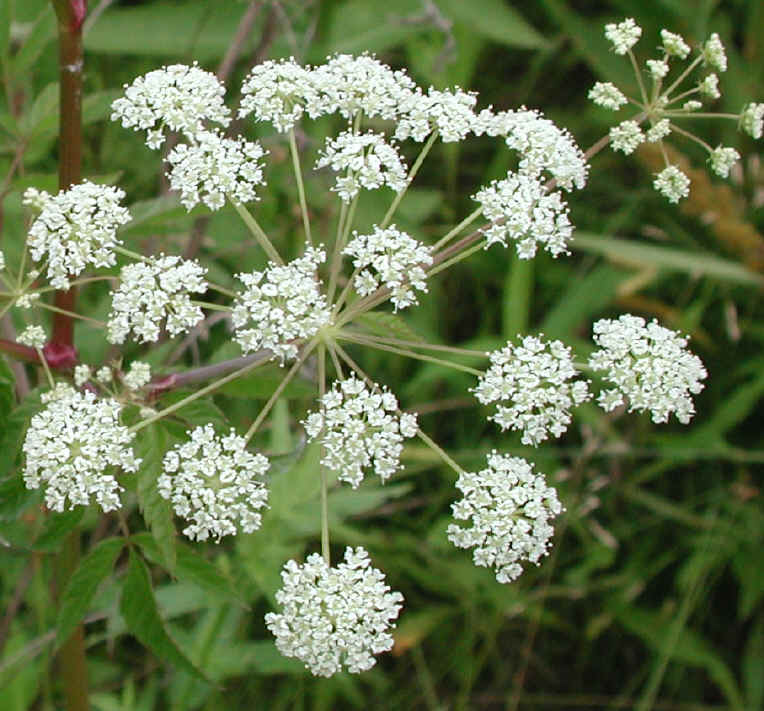

*Water hemlock can cause seizures and there are case reports of death. It looks a lot like Queen Ann’s Lace.

*Poison Ivy/Oak/Sumac. These plants contain urushiol.
Don’t eat green tomatoes or green potatoes. These can cause GI irritation and hallucinations.
Ackee fruit can cause elevated ammonia level with CNS alteration and GI distress.
Colchicine is contained in glory lilly and can cause multi-organ failure.
Ricin is extracted from the castor bean. Jequirity pea is similar to ricin but 30 times stronger. Both can cause hemorrhagic gastroenteritis and multi-organ failure.
Apple seeds in large amounts can be fatal due to cyanide toxicity.
Apple seeds and castor beans are not toxic if swallowed whole.
Bottom line to this lecture: Don’t eat plants that aren’t sold in the vegetable section of your grocery store. If you eat plants from other places bad things can happen.
Regan Five Slide Follow Up
23 yo male fell while drinking and using heroin 2 days prior to ED visit . Patient presented to the ED with left side weakness. Patient also had left side facial swelling and left arm and leg swelling.
Lab testing showed dark urine and a serum CK of 58, 000. Neuro work up was basically negative. It turned out that patient had been laying on the floor for a prolonged period of time. This resulted in rhabdomyolysis.
Rhabomyolysis is diagnosed with CK level 5X normal. Large blood in urine is a clue to rhabdomyolysis that should be followed up with a measured CK level. CK levels>5000 increases risk of renal injury.
Treatment is aggressive IV fluids. Alkalinize urine with bicarb (3 amps of bicarb in 1 Liter of D5W) . There is no clear evidence that bicarb drip has an advantage over IV saline.
Orthopedic Lab
We had 5 stations to work on various exam and reduction techniques.
ICEP and SAEM Conference Pictures
SAEM SONOGAMES Team Drs Hart, Htet, Ede.

ICEP Lindsay Purnell
Jennifer Cash at ICEP
Rachel Kadar at ICEP